Python使用PyMySQL操作MySQL数据库(附详细示例)
使用Python爬取数据过程中,会遇到需将爬取的数据存储到数据库中的场景,本文介绍如何使用PyMySQL模块,连接MySQL数据库,实现对数据库的操作。
PyMySQL GitHub地址
https://github.com/PyMySQL/PyMySQL
GitHub有具体连接和操作MySQL数据库的示例,喜欢的同学可到官方页面学习。
一、创建示例数据库
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
-- 1、创建示例数据库 create database python_data1 default character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_unicode_ci; -- 2、创建数据库用户,并授权 create user 'python'@'localhost' identified by 'password'; grant all privileges on python_data1.* to 'python'@'localhost' identified by 'password'; grant all privileges on python_data1.* to 'python'@'127.0.0.1' identified by 'password'; -- 3.1 创建数据库表 use python_data1; create table crawled_data1( id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键', data_source varchar(100) comment '数据来源', field_group varchar(32) comment '字段分组', field_name varchar(50) comment '字段名称', field_value varchar(50) comment '字段值', created_date datetime comment '创建时间') comment 'Python爬取的数据表1'; -- 3.2 创建索引 create index crawled_data1_data_source on crawled_data1(data_source); create index crawled_data1_field_group on crawled_data1(field_group); |
二、安装PyMySQL
|
1 |
pip3 install PyMySQL |
三、PyMySQL连接数据库进行简单查询
方式1:直接将数据库连接信息写在代码中
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
import pymysql.cursors # 定义数据库连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='python', passwd='password', db='python_data1', charset='utf8mb4', cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # noinspection PyBroadException try: cursor = conn.cursor() # 通过cursor创建游标 sql = 'select * from crawled_data1;' # 创建sql 语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 执行sql语句 results = cursor.fetchall() # 获取所有记录列表 print(results) for data in results: # 打印结果 print(data) cursor.close() # 关闭游标连接 except Exception: print('Query failed!') conn.close() # 关闭数据库连接 |
方式2:将数据库连接信息写在配置文件中(从配置文件读取MySQL参数)
由于直接将密码写在代码中,有一定的安全风险,故将密码写到配置文件中,Python从配置文件中读取MySQL数据库的连接信息。
(1)新建config_mysql_localhost.ini配置文件,存放到指定目录:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
[MySQL_INFO] host = localhost port = 3306 user = python passwd = password db = python_data1 charset = utf8mb4 |
(2)Python代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
import pymysql.cursors import configparser class ReadConfig: def __init__(self, _config_path): self.cf = configparser.ConfigParser() self.cf.read(_config_path) def get_mysql_info(self, _param): _value = self.cf.get("MySQL_INFO", _param) return _value config_path = 'E:\\P_Python\\PycharmProjectsConfig\\config_mysql_localhost.ini' mysql_host = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('host') mysql_port = int(ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('port')) mysql_user = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('user') mysql_passwd = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('passwd') mysql_db = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('db') mysql_charset = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('charset') # 定义数据库连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host=mysql_host, port=mysql_port, user=mysql_user, passwd=mysql_passwd, db=mysql_db, charset=mysql_charset, cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # noinspection PyBroadException try: cursor = conn.cursor() # 通过cursor创建游标 sql = 'select * from crawled_data1;' # 创建sql 语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 执行sql语句 results = cursor.fetchall() # 获取所有记录列表 print(results) for data in results: # 打印结果 print(data) cursor.close() # 关闭游标连接 except Exception: print('Query failed!') conn.close() # 关闭数据库连接 |
四、PyMySQL连接数据库进行插入操作
下述例子,执行内容为:每10秒钟,从https://www.tianqi.com/抓取青岛市天气信息,插入数据库中,插入字段包括城市、天气、当前温度、最低最高温度。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 |
import pymysql.cursors import configparser import requests import re import random import uuid import datetime import time from bs4 import BeautifulSoup class ReadConfig: def __init__(self, _config_path): self.cf = configparser.ConfigParser() self.cf.read(_config_path) def get_mysql_info(self, _param): _value = self.cf.get("MySQL_INFO", _param) return _value # Connection选项设为close,用于解决连接池一直不关闭问题 # 报错:requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: HTTPConnectionPool(host='xxx.com', port=80): Max retries exceeded def get_content(url, agent): random_agent = random.choice(agent) headers = {"User-Agent": random_agent, 'Connection': 'close'} content = requests.get(url, headers=headers).content return content if __name__ == '__main__': config_path = 'E:\\P_Python\\PycharmProjectsConfig\\config_mysql_localhost.ini' mysql_host = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('host') mysql_port = int(ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('port')) mysql_user = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('user') mysql_passwd = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('passwd') mysql_db = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('db') mysql_charset = ReadConfig(config_path).get_mysql_info('charset') # 定义浏览器 user_agent = [ "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/76.0.3809.132 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:68.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/68.0", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; Trident/7.0; Touch; rv:11.0) like Gecko", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/64.0.3282.140 Safari/537.36 Edge/17.17134", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/61.0.3163.79 Safari/537.36 Maxthon/5.2.7.2000" ] # 定义数据库连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host=mysql_host, port=mysql_port, user=mysql_user, passwd=mysql_passwd, db=mysql_db, charset=mysql_charset, cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) crawl_url = 'https://www.tianqi.com/qingdao/' # 循环执行,每10秒插入1次 while True: # noinspection PyBroadException try: url_content = get_content(crawl_url, user_agent) soup = BeautifulSoup(url_content, 'html.parser') city = soup.find('dd', class_='name').h2.text weather = soup.find('dd', class_='weather') weather_now = weather.span.b.text temp_now = weather.p.b.text temp_range_long = weather.span.text split1 = re.search(r'\d+', temp_range_long).group() split2 = split1[0] position = temp_range_long.index(split2) temp_range = temp_range_long[position:] data_source = 'www.tianqi.com' field_group = uuid.uuid1().hex created_date = str(datetime.datetime.now()) print('time: ' + created_date + ' uuid: ' + field_group + ' ' + city + ' ' + weather_now + ' ' + temp_now + ' ' + temp_range) # 通过cursor创建游标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 定义要执行的sql语句 sql = 'insert into crawled_data1(data_source,field_group,field_name,field_value,created_date) values (%s,%s,%s,%s,%s);' sql_data = [ (data_source, field_group, 'city', city, created_date), (data_source, field_group, 'weather_now', weather_now, created_date), (data_source, field_group, 'temp_now', temp_now, created_date), (data_source, field_group, 'temp_range', temp_range, created_date) ] # 拼接并执行sql语句 cursor.executemany(sql, sql_data) conn.commit() cursor.close() # 关闭游标连接 print('time: ' + created_date + ' uuid: ' + field_group + ' insert success!') except Exception as exception_info: print(exception_info) time.sleep(10) conn.close() # 关闭数据库连接,一直循环的情况下,不会执行到这行代码 |
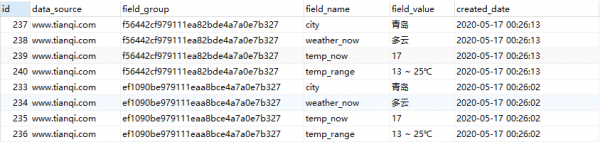
4.1 查询插入数据库的信息(原始)
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
select * from crawled_data1 t1 where 1 = 1 and t1.data_source = 'www.tianqi.com' order by t1.created_date desc,t1.id; |
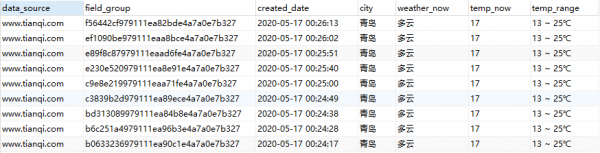
4.2 查询插入数据库的信息(转为横向)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
select t1.data_source, t1.field_group, t1.created_date, t1.field_value as city, t2.field_value as weather_now, t3.field_value as temp_now, t4.field_value as temp_range from crawled_data1 t1 left join crawled_data1 t2 on t1.field_group = t2.field_group and t2.field_name = 'weather_now' left join crawled_data1 t3 on t1.field_group = t3.field_group and t3.field_name = 'temp_now' left join crawled_data1 t4 on t1.field_group = t4.field_group and t4.field_name = 'temp_range' where 1 = 1 and t1.data_source = 'www.tianqi.com' and t1.field_name = 'city' order by t1.created_date desc; |